What Is Battery Vs Assault - Assault and battery are two crimes that are often prosecuted together, although they are separate crimes with different elements. Although modern jurisdictions often combine assault and battery into one statute called assault, the crimes are still distinct and often classified separately. The Model Penal Code calls both crimes assault, simple and aggravated (Model Penal Code § 211.1). However, the Model Penal Code does not distinguish between assault and battery for degree purposes. This section reviews the elements of both crimes, including potential defenses.
Battery is a crime that contains the elements of criminal act, criminal intent, attendant circumstances, causation and harm as discussed in the subsections below.
What Is Battery Vs Assault

The criminal action element required for battery in most jurisdictions is unlawful touching, often defined as physical contact (720 ILCS § 12-3, 2011). That criminal act is the element that distinguishes assault from battery, although a person can be convicted of both crimes if he commits separate acts supported by reasonable intent. The perpetrator may touch the victim with an instrument, such as shooting the victim with a gun, or hit the victim with a thrown object, such as rocks or a bottle. The offender may also touch the victim with a vehicle, knife or substance, such as spitting on the victim or spraying the victim with a hose.
Buy Assault And Battery: Report Of The Trials Of The Causes Of Elisha Jenkins Vs. Solomon Van Rensselaer, Solomon Van Rensselaer V. John Tayler, The Same ... Before Arbitrators, At Albany, August
Recall an example from Chapter 1, "Introduction to Criminal Law," where Chris, a newly hired employee at McDonald's, spills steaming coffee on the hands of his customer, Geoff. Although Chris did not touch Geoff with any part of his body, he did illegally insert a touching substance.
Depending on the jurisdiction, the criminal intent element required for battery varies. At early common law, battery was intentional or touching. Many states follow the common law approach and require specific intent or willfulness, or general intent or willfulness (Fla. Stat. Ann. § 784.03, 2011). Others include reckless intent (K.S.A. § 21-3412, 2011), or reckless intent (R.I. Gen. Laws § 11-5-2.2, 2011). Jurisdictions involving negligence or reckless intent generally require actual injury, serious bodily injury, or the use of a deadly weapon. The Model Penal Code requires intentional, willful, or negligent infliction of bodily injury on another, or recklessly inflicting "bodily injury on another by means of a deadly weapon" (Model Penal Code § 211.1(1) (b)). . If negligent intent
Review the example with Chris and Geoff in Section 10 "Battery Law Example." Suppose that Chris spills hot coffee on Geoff's hand when Chris is trying to multitask and at the same time he spills the coffee. Chris's act of physically touching Geoff with hot coffee can be supported by a negligent intent because Chris is a new employee and possibly unaware of the risk of spilling coffee while multitasking. If the state in which Chris's discharge occurs does not include negligent intent in its battery statute, Chris likely
, Chris would not be on trial for battery unless the coffee caused Geoff's hand to be severely burned; Hot coffee cannot kill and would probably not be considered a lethal weapon.
Actual Bodily Harm Cases
The current circumstantial element required for battery in most jurisdictions is that the touching occur without a victim
. Thus the victim's consent may serve as a failure of proof or affirmative defense in certain factual situations.
Recall from Chapter 5 "Criminal Defense, Part 1" when Alan tackled Brett during a high school football game, causing Brett to suffer a serious injury. Although Allen intentionally touched Brett, and the result is serious bodily injury, Brett voluntarily consented to the touching by participating in a sporting event where physical contact occurs.
. Thus the present circumstantial element for battery is absent and Allen may not be subject to prosecution for that offense.
Difference Between Aggravated Assault And Aggravated Battery In Oklahoma
In addition to consent, there are valid and aggravated defenses to battery, which are discussed in detail in Chapter 5 "Criminal Defenses, Part 1" and Chapter 6 "Criminal Defenses, Part 2". To summarize and review, valid defenses to battery are self-defense, defense of property and residence, and legitimate fear of criminals. An aggravated defense to battery that Chapter 6 "Criminal Defenses, Part 2" explores is the insanity defense. There is another flawless defense for the battery
Of a parent's child which is generally regulated by law and varies from state to state (Kidjacked.com, 2011).
The defendant's criminal act must be the actual and legal cause of the damage, which is defined in Section 10 "Battery Damages."
Contact (720 ILCS § 12-3, 2011). Some jurisdictions require actual injury to the victim (Ala. Code § 13A-6-21, 2011). The severity of the injury may increase the grading, as discussed in Section 10 "Battery Grading".
Assault Vs Battery: What's The Difference?
Review the example in Section 10 "Example of an Act of Battery" where Chris spills hot coffee on Geoff's hand. If Chris and Geoff are in a position that needs it
As an element of battery to the victim, Chris would not be subject to prosecution for that crime unless the hot coffee hurt Geoff's hand. If Chris and Geoff are in a position that allows harm
Contact, as long as the battery intent element is present, Chris can be charged or convicted of battery, as discussed in Section 10 "Battery Intent."
At early common law, battery was a misdemeanor. The Model Penal Code classifies battery (called simple assault) as a misdemeanor unless "committed in a fight or disturbance committed by mutual consent, in which case it is a minor misdemeanor" (Model Penal Code § 211.1 (1)). Grades of Model Penal Code
Simple Vs. Aggravated Assault And Battery
Battery (also called aggravated assault), which is battery that causes serious bodily injury or bodily harm by means of a deadly weapon, as a felony of the second or third degree (Model Penal Code § 211.1(2)). Many states follow the Model Penal Code approach by classifying battery as a misdemeanor (720 ILCS § 12-3, 2011) and battery that causes bodily injury as a gross misdemeanor or felony (720 ILCS § 12-3, 2011). 4) as a wrongful act or causing emotional injury. ). , 2011). Additionally, battery supported by a higher degree of intent — such as the intent to cause serious bodily injury or maim or maim — is often given a higher degree (Ala. Code § 13A-6-20, 2011). Other factors that may increase the battery rating are the use of a firearm (R.I. Gen. Laws § 11-5-2, 2011), the commission of a battery during the commission or the attempted commission of a serious or violent crime (Ala. Code § went 13A) —6-20, 2011), the victim's helplessness (Wis. Stat § 940.16(6), 2011), and a teacher (Wis. Stat. § 940.16(5), 2011) or a police officer (Wis. Stata ) against battery § 940.20(2), 2011).
Assault is a crime that has the elements of criminal act and intent. Some types of attack also have a causation and damage element, as discussed in Section 10 "Dangerous Battery Attacks."
Two types of attacks are recognized. In some jurisdictions, assault battery is attempted. In other jurisdictions, assault is threatened battery. The Model Penal Code criminalizes both attempted battery and threatened battery (Model Penal Code § 211.1). The elements of both types of assault are discussed in Section 10 "Attempted Battery and Threatened Battery Assault".
An attempted battery attack is an attack that involves every element of battery except physical contact. The elements of attempted battery assault are a criminal act supported by criminal intent. There is no need for causation or damages because
What Are The Differences Between Assault And Battery?
Crimes require no damages. Although attempted battery assault is allowed the same defense of consent as battery, this is not as common with assault as it is with battery, so most statutes are attendant to the victim's lack of consent. There is no circumstantial element.
Make physical contact with the victim but is missing for some reason. It could be a thrown object that never hits its target, a shot that misses, or a punch that doesn't connect. In some states, the defendant must have the present ability to cause harmful or offensive physical contact, even if the contact never occurs (Cal. Penal Code § 240, 2011). The present skill requirement is merely an extension of the rule that offenses of abetment must go beyond mere preparation. In most jurisdictions, the elements of a criminal action are measured by the substantial step test of the Model Penal Code described in detail in Chapter 7 "Parties to a Crime" (State v. Matthews, 2011). To summarize, the substantial step test requires that the defendant take substantial steps to complete the battery, and that the defendant's actions must be conclusively corroborating the defendant's criminal intent (Model Penal Code § 5.01). .
Diana points a loaded pistol at her ex-boyfriend Dan, says, "Prepare to die, Dan," and pulls the trigger. Fortunately for Dan, the gun malfunctions and doesn't fire. Diana may have attempted a battery attack. Diana took every step necessary to complete the battery, and her conduct in pointing the pistol at Dan and pulling the trigger strongly corroborated her criminal intent. Additionally, it appears that Diana had the current ability to shoot Dan because her gun was loaded. Thus Diana could be convicted and prosecuted for the crime
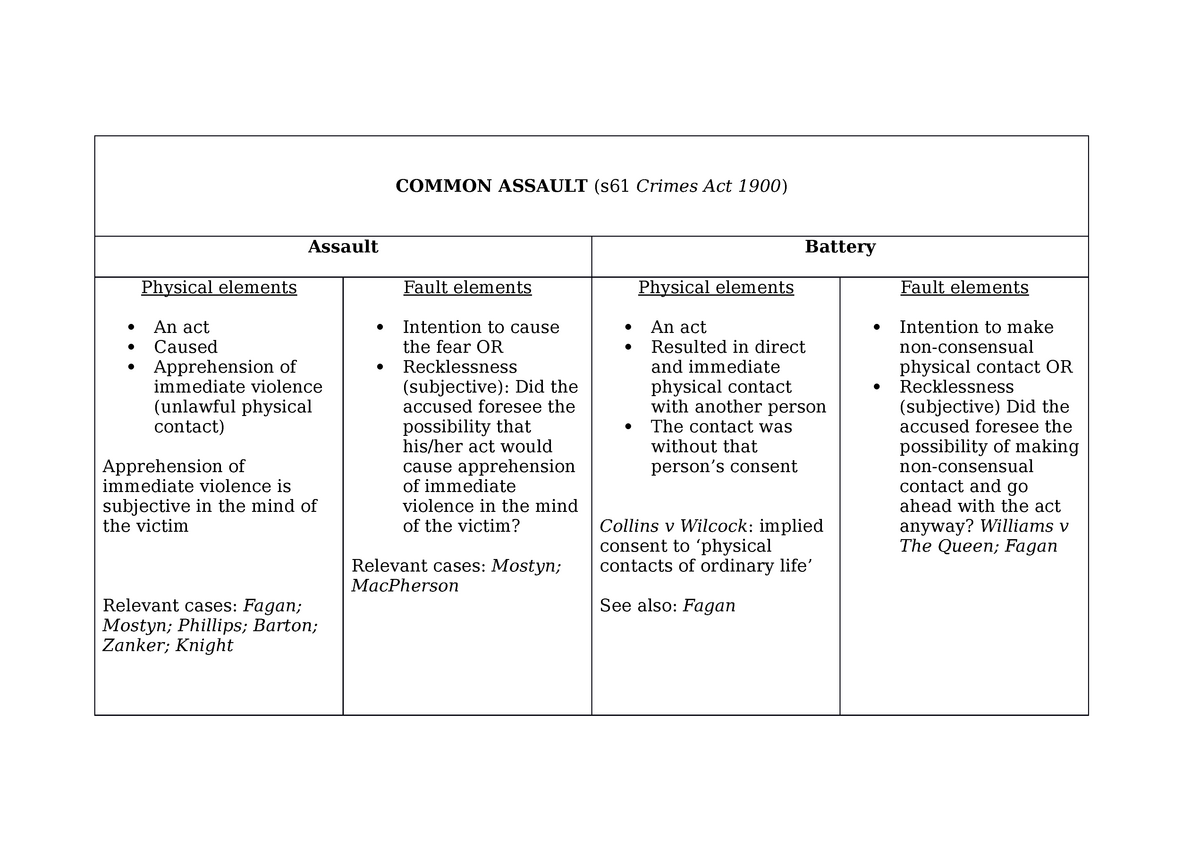
What is assault and battery, what is aggravated assault and battery, what is considered assault and battery, what is battery assault, what is assault and battery charge, what is assault vs battery, what is the punishment for assault and battery, what is battery assault charges, what is the penalty for assault and battery, what is difference between assault and battery, what is domestic assault and battery, what is the definition of assault and battery
